Motivation
We have table Student{ID, First_name, Last_name, Age} that contains 1M records
Now, if we want to search about student that have ID = x, we will scan all blocks to search about it. (Linear search)
What if we have file that contains ID and record address? it's more optimal than Linear search and index file size is less than data file size
Note that index file must be sorted
Overview
Indexing improve search query and solve problems such as data file can't load it in the memory
Improve means try to minimize number of disk access
Indexing
- Technique used to improve search query and may be consider it as auxiliary file
Index file structure
- Search key value
- Address (record pointer)
Indexes can be characterize
Sparse index
- Has index for only some entries (record)
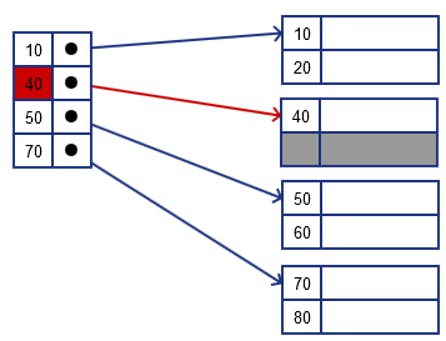
- Is applicable if data file is sequential (ordered)
- Less space as it's not store index for all entries
- Less maintenance for insertion and deletion operation
Dense index
- Has index for all entries (record)
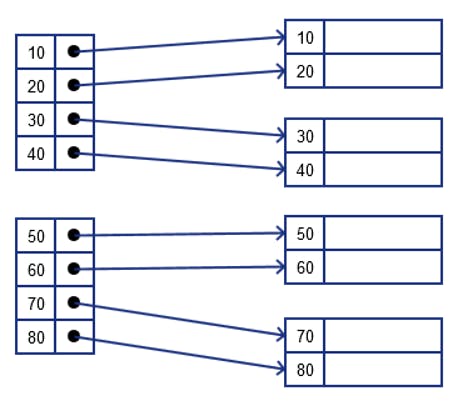
Faster than sparse as it's has index for all entries
- More Space
- More maintenance for insertion and deletion operation
Type of index
Single level index
- Primary index
- Secondary index
Multi-level index
- B tree
- B+ tree
Constraints to build primary index file
- Data file must be sorted on search key
- Always search key is Primary key
Note We can't build more than one primary index file as data file must be sorted on search key (PK)
Constraints to build secondary index file
- Data file not sorted on search key
- search key is any attribute other than primary key and may be candidate key
Note We can build more than one secondary index file
Primary key Vs Candidate key
Primary key
- Primary Key is a set of attributes (or attribute) which uniquely identify the tuples in table
Candidate key
- Is a set of attributes (or attribute) which uniquely identify the tuples in relation or table
- Candidate key’s attributes can contain a NULL value which opposes to the primary key
- There is one or more candidate key in any table
Example
Student{ID, First_name, Last_name, Age}
Here only ID can be primary key because the name, age and address can be same, but ID can’t be same.
Note any Primary key is also candidate key and the opposite is not true
Problems with indexing
- Insertion, deletion and update operation not optimal as after each operation tree must be balanced tree
Finally, what about if index file can't load it in the memory?
See You Later
